
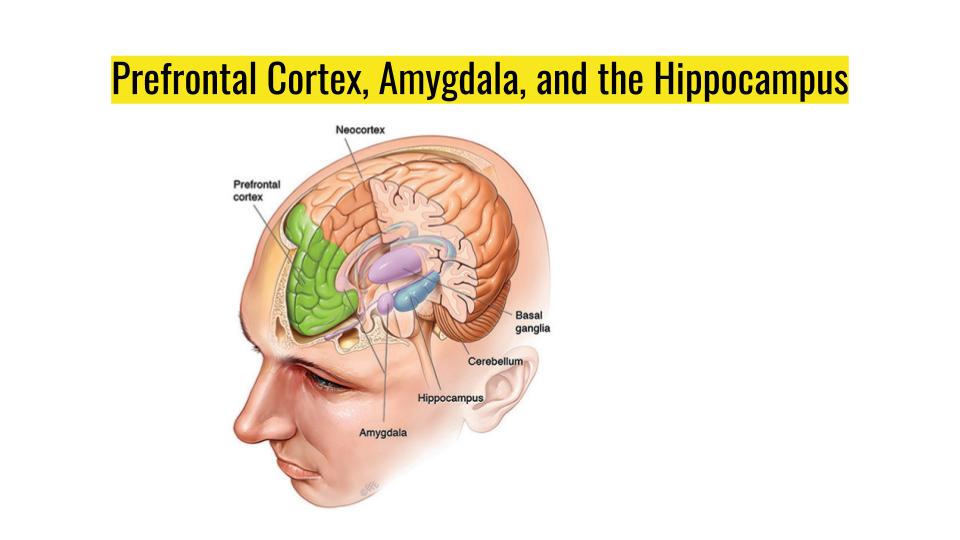
It is part of a system that processes "reflexive" emotions like fear and anxiety.Ĭingulate Gyrus: Plays a role in processing conscious emotional experience.įornix: An arch-like structure that connects the hippocampus to other parts of the limbic system.įrontal Lobe: Helps control skilled muscle movements, mood, planning for the future, setting goals, and judging priorities. Glossary of TermsĪmygdala: Limbic structure involved in many brain functions, including emotion, learning and memory. The hippocampus is one of the first areas affected by Alzheimer's disease. As the disease progresses, damage extends throughout the lobes. The limbic system consists of a number of structures, including the fornix, hippocampus, cingulate gyrus, amygdala, the parahippocampal gyrus, and parts of the thalamus. The image on the right is a side view showing the location of the limbic system inside the brain. This false alarm happens because the goal is to survive, there is an advantage to react first and think later.The image on the left is a side view of the outside of the brain, showing the major lobes (frontal, parietal, temporal and occipital) and the brain stem structures (pons, medulla oblongata, and cerebellum). This means even vague similarities can triggers fear signals in the brain, alerting you of a threat. If any key elements are even vaguely similarthe sound of a voice, the expression on a faceyour amygdala instantaneously lets loose its warning sirens and an accompanying emotional explosion. For when the amygdala tries to judge whether a current situation is hazardous, it compares that situation with your collection of past emotionally charged memories. It is the amygdala that is responsible for the surge of fury that floods your body when you see someone who looks even vaguely like your former mate.Īnd “vaguely” is the operative word here. For example, the prefrontal cortex will remember what your ex-partner looks like, that petite brunette who dumped you for a new lover. The amygdala’s emotional response provides a mechanism to work around the limitation of the prefrontal cortex’s reasoning.

There is an instinctual reflex to stop and freeze when there is a sudden loud noise. Automatically, the restaurant comes to a dramatic halt as everyone simultaneously falls to a hush. Suddenly a waiter drops a tray with several glasses, which crashes and shatters as they hit the floor.

Within milliseconds, men explode with rage or freeze in fear, well before their prefrontal cortex can even grasp what is happening.įor example, say youre in a crowded restaurant and the noise of chatter from dozens of conversations fills the air. Men in the hunter-gatherer world needed a large amygdala to quickly respond when scanning the terrain for potential danger: Is this bad? Could it hurt me? If the information registered as dangerous, the amygdala broadcasts a distress signal to the entire brain, which in turn, triggers a cascade of physiological responsesfrom a rapid heart rate to jacked-up blood pressure to tense muscles to the release of adrenaline.
Their powerful emotional outbursts of anger, when seen through the hunter gatherer lens, are helpful to come out on top during a confrontation. Men are hard wired for hunting, competition and dominance. This makes sense if you consider the energy needed to be vigilant for self-protection.

Scientists have discovered that men have a larger part of their brain devoted to emotional responses and a smaller region for logical thinking than women. Stereotypically, women are thought of as emotional and men as logical, but biology reveals this as false.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
